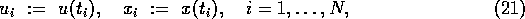
For the sake of simplicity, we now assume that n = 1 and l = 1. In this section, we will use the notations
and
The Lagrangian of the nonlinear program of the discretized problem from Sec. 2 can then be written as
with 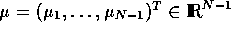 ,
,
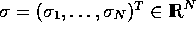 and
and 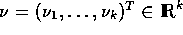 .
A solution of the nonlinear program fulfills the necessary first order
optimality conditions
of Karush, Kuhn, and Tucker, cf.,
e. g., [9]. Among others, these are
.
A solution of the nonlinear program fulfills the necessary first order
optimality conditions
of Karush, Kuhn, and Tucker, cf.,
e. g., [9]. Among others, these are
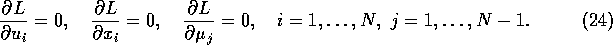
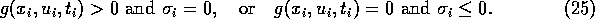
As the ``fineness'' of the grid, we define
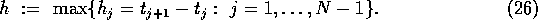
In detail, we find for  ,
,
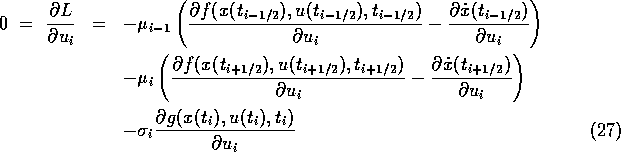
Using the basic relations (23) -- (31) of [18] and the notation from (21), (22), we obtain after some calculations and by using the chain rule of differentiation
Letting  and keeping
and keeping  fixed, we have
fixed, we have
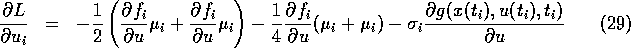
and finally
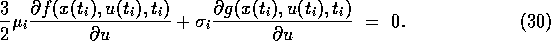
This equation is equivalent to the
condition (19).
On the other hand, for 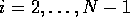 ,
,
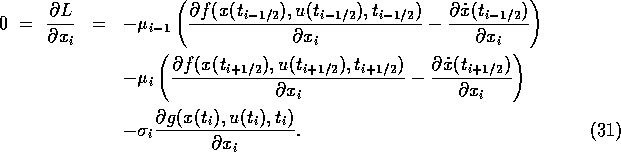
Using again the basic relations (23) -- (31) of [18] and the notation from (21), (22), we obtain after some calculations and by using the chain rule of differentiation
For convenience, we now suppose an equidistant grid, i.e.\
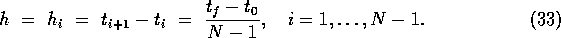
Now letting 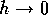 and keeping
and keeping 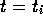 fixed, we have
(cf. [18])
fixed, we have
(cf. [18])
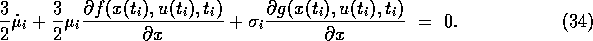
This equation is equivalent to the
adjoint differential equation (18).
Similar results hold for a non-equidistant grid under additional
conditions and for n > 1.
They can also be extended to more general problems.