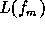 of free running oscillators
can be calculated by solving Eq. (
of free running oscillators
can be calculated by solving Eq. (
The single-sideband phase noise 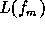 of free running oscillators
can be calculated by solving Eq. (
of free running oscillators
can be calculated by solving Eq. (![]() )
and using a perturbation approach (Kärtner [
)
and using a perturbation approach (Kärtner [![]() ])
])
The first term on the right hand side of Eq. (![]() ) describes
the phase noise
caused by the white noise sources.
) describes
the phase noise
caused by the white noise sources.  is the left-sided
eigenvector of the eigenvalue 1
of the fundamental matrix
is the left-sided
eigenvector of the eigenvalue 1
of the fundamental matrix 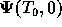 .
The matrix
.
The matrix 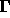 denotes the correlation
matrix of the white noise sources. The second term
of Eq. (
denotes the correlation
matrix of the white noise sources. The second term
of Eq. (![]() ) describes the phase noise
caused by the baseband noise.
The factor
) describes the phase noise
caused by the baseband noise.
The factor 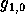 characterizes
the upconversion of the baseband noise to the carrier frequency
characterizes
the upconversion of the baseband noise to the carrier frequency
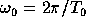 .
The
modulation of the
.
The
modulation of the 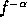 noise source due to the oscillation is taken
into account as well as the upconversion of the baseband noise caused by
the nonlinearities in the circuit.
The factor c is derived from baseband noise measurements.
noise source due to the oscillation is taken
into account as well as the upconversion of the baseband noise caused by
the nonlinearities in the circuit.
The factor c is derived from baseband noise measurements.
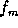 is the offset frequency
where the single-sideband phase noise is to be calculated.
The functions
is the offset frequency
where the single-sideband phase noise is to be calculated.
The functions 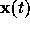 and
and 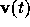 depend on
the design parameters
depend on
the design parameters 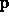 of the circuit
(e.g., capacitors and inductors of the linear network)
by the system of 2 n nonlinear
differential equations derived from (
of the circuit
(e.g., capacitors and inductors of the linear network)
by the system of 2 n nonlinear
differential equations derived from (![]() )
)
and 2n+1 boundary conditions